8 Ways the Plastics Industry is Using 3D Printing
Plastics processors are finding applications for 3D printing around the plant and across the supply chain. Here are 8 examples to look for at NPE 2024.
Once relegated to rapid prototyping, 3D printing technology has now advanced far beyond the design studio. Machines have improved and material options have widened. Today molders, moldmakers and OEMs alike are turning to this layer-by-layer production technology to save time, serve new markets and even fill supply chain gaps.
At NPE 2024: The Plastics Show, 3D printing and additive manufacturing (AM) suppliers will be highlighted in the Advanced Manufacturing Zone, while AM users will take to the stage for Wednesday’s 3D Printing Workshop. But keep an eye out for promising developments and applications across the show floor, including:
1. Mold Tooling
Lead time delays for molded parts often originate from difficulties with sourcing tooling. 3D printing makes it possible to accelerate mold development and simplify design changes down the line. If a new design is needed, 3D printing offers a faster route to a new tool and even the chance to repair or modify an existing one. While metal 3D printing methods, such as laser powder bed fusion, have historically been the most common techniques applied to mold tooling, there are new innovations to explore in terms of more accessible metal printing methods and short-run molds made from other materials such as polymer composites.

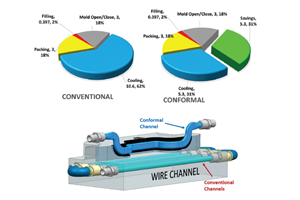
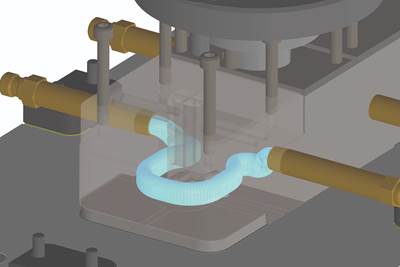
The clear model in the center shows the conformal cooling lines inside the metal 3D printed mold on the right, used to produce the plastic part on the left.
2. Robot End Effectors
Cobots, pick-and-place robots and other automation can make plastics processing more productive, but in most cases these additions require specialized end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) and other fixturing. 3D printing can be applied to produce vacuum grippers and other specialized end effectors for handling parts. These devices can integrate vacuum lines, wire harnesses and other features to simplify assembly, and tend to be lighter weight than conventional options.
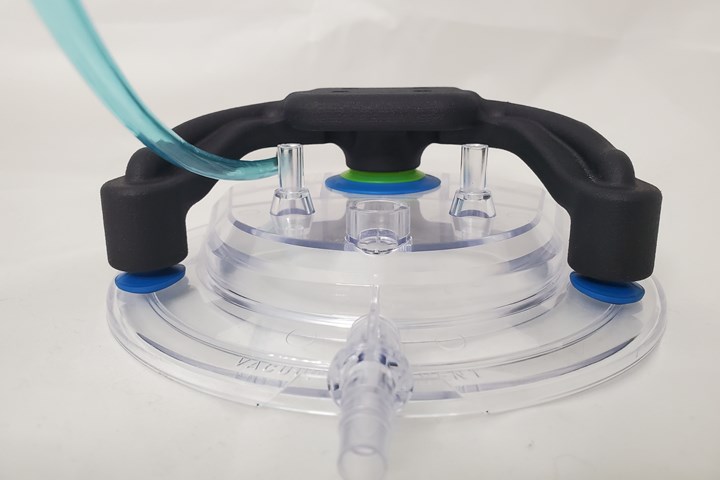

This 3D-printed EOAT incorporates air lines for vacuum and pressure into its design.
3. Fixtures
3D-printed nests for CMM inspection can be created using the part’s existing CAD model, similar to the process for designing a mold.
Affordable desktop 3D printers make it possible to create affordable items for plant use such as inspection fixtures, assembly tools and check gages. CMM nests, for example, can be developed using mold design tools to generate the inverse of the part and arrive at a 3D-printable fixture design. As an added bonus, once fixtures have been developed for 3D printing, they can be saved as digital files. Should one be damaged or go missing, it can be quickly replaced by simply printing another.
4. Prototyping and Product Development
3D printing still plays a valuable role for rapid prototyping, as it is often the fastest way to get a look-and-feel prototype or iterate design ideas. However, the technology has advanced to the point that, with the right material and printer, a prototype can often be used just like a production part. Brackets, electronics enclosures, ducts, components of medical devices and more have made this leap.

These smart ski goggles were developed with a 3D printed electronics enclosure. Originally meant as a prototype, the 3D printed assembly has since been used in sale units as well.
5. Bridge Production

This air diverter for a youth motorbike was designed for injection molding, but bikes produced before the mold tooling was ready used 3D printed parts like this.
The need for tooling adds automatic lead time to producing a new molded part, but 3D printing can enable a manufacturer to jump straight into production while waiting for that tooling. This means that new products can be launched into the marketplace sooner, and brand owners can get feedback before committing to the expense of a mold. The bridge need not start at the beginning of a product’s life span, either — many companies are now turning to 3D printing to bridge gaps due to supply chain disruptions as well.
6. Mass Customization
The digital nature of 3D printing makes it possible to easily adjust a base product design via software to suit the specific customer or application. The technology can be applied to produce everything from custom medical devices such as splints and hearing aids to consumer products like shoe insoles and sporting equipment tailored to the buyer.
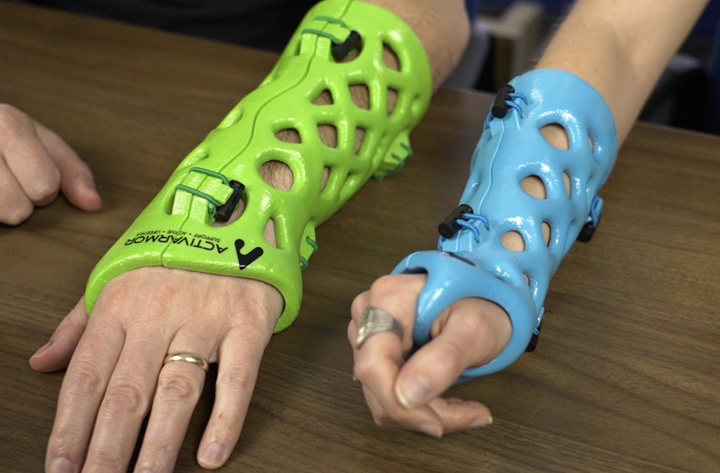

3D printing makes it possible to support custom geometry and tweaks to a product design like a forearm cast, so that each part can be tailored to the user.
7. Digital Inventory
These autobody clips are 3D printed on demand in groups as an alternative to storing extras in physical inventory.
Files for 3D printing are more easily stored than physical parts, leading major OEMs, military branches and government agencies to adopt the technology as a way of sourcing spare parts and items needed for system maintenance. Digital inventory parts like clamps, clips and brackets can be 3D printed as needed, saving the hassle and expense of storing extras or keeping track of tooling. Even better, digital inventory can also be distributed. By working with manufacturing partners or placing printers at different facilities, organizations can produce these parts near where they will be used.
8. Serial Production
3D printing is a viable production choice for a variety of products, particularly where printing enables geometric complexity or other advantages. While 3D printing is capable of continuous production of tens of thousands of pieces, it is equally applicable to smaller batches of parts needed less frequently — with no minimum order quantity. Production use cases for this technology include brackets, phone cases, valves, medical implants, packaging solutions and much, much more.
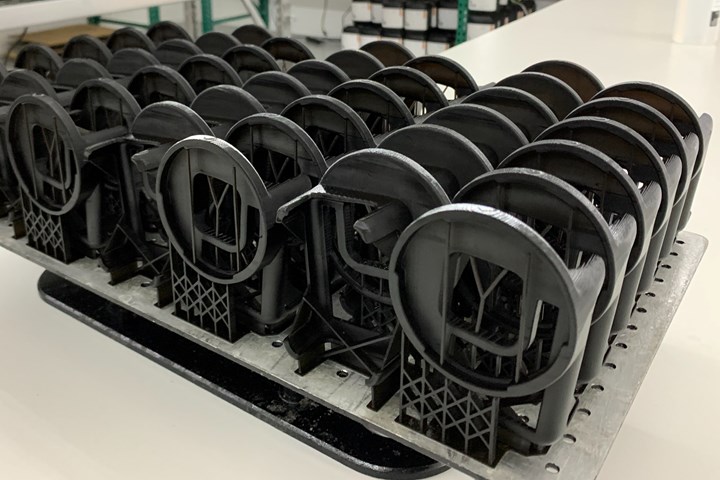

These phone case components are 3D printed in a machine that can produce several hundred of these parts per day; scaling production to higher quantities means simply adding additional machines.
Related Content
Products and Services for Multiple Moldmaking Needs
New year, new technology roundup! Featured here is a collection of product offerings, from profile milling cutters to industry-specific CAD/CAM software to innovative hot work tool steels.
Read MoreVIDEO: How can 3D Printed Tooling Improve Injection Mold Venting?
Proper venting is one of a mold builders toughest challenges as molders struggle to keep vents free flowing in production. Learn how to apply 3D printing to mold venting and the benefits of additive venting inserts.
Read MoreHow to Use Thermal Management to Improve Mold Cooling
A review of common mold cooling issues and possible solutions, including 3D printing applications.
Read MoreVariable Density-Coated Tool Steel for High-Wear Molds
A mold builder can have an abundance of venting and fully dense solid areas in steel by using variable density sintering to eliminate gas trap defects in high-wear molds.
Read MoreRead Next
A 3D Printing Retrospective
A personal review of the evolution of 3D printing in moldmaking throughout the past 25 years.
Read MoreHow to Supply Cooling to Additive Tooling
Additive tooling provides limitless options for cooling a mold’s difficult-to-cool areas.
Read MoreHow Hybrid Tooling Accelerates Product Development, Sustainability for PepsiCo
The consumer products giant used to wait weeks and spend thousands on each iteration of a prototype blow mold. Now, new blow molds are available in days and cost just a few hundred dollars.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)
















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)

_300x250 1.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)
.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)