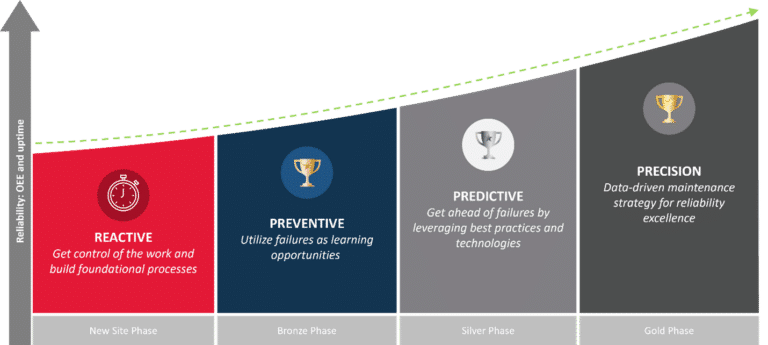
There are several different types of maintenance strategies that may be used in a successful manufacturing operation. In general, most facilities will draw upon four types of maintenance strategies:
- Corrective maintenance (or reactive maintenance)
- Preventive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance
- Precision maintenance
Each type of maintenance is best used in a specific scenario (or scenarios), and nearly all manufacturers will use some combination of the above in the course of their operations (as opposed to just one particular strategy from the list). Here, we will examine the different types of maintenance strategies in greater depth.
Corrective maintenance (or reactive maintenance)
Corrective maintenance, also called reactive maintenance or run-to-failure maintenance, is maintenance that is initiated when failure or near-failure is noticed, and it is typically carried out immediately or in short order. As a maintenance strategy, corrective maintenance is inefficient and costly in terms of resources, spare parts and potential downtime, since maintenance only occurs at or near a failure state.
While corrective maintenance should not be an organizational strategy, it is almost always necessary at some point in the course of operations, even with one of the more effective equipment maintenance strategies in place.
Preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance is regularly scheduled maintenance that occurs in accordance with OEM recommendations, or at another regular interval as defined by the organization. This type of maintenance generally occurs whether it is needed or not, and as such, can be inefficient in terms of replacing equipment that is still useful. On the flip side, preventive maintenance is not able to detect more immediate maintenance issues and may result in unplanned downtime. While preventive maintenance should not be the sole strategy in use, it does provide benefits, and should be incorporated into most organizational maintenance plans.
Predictive maintenance
The difference between preventive and predictive maintenance is that predictive maintenance takes a more proactive approach, drawing on data, analytics and real-time performance metrics to identify impending maintenance needs and schedule diagnosis and remedy well before unplanned downtime occurs. In contrast to the above two asset maintenance strategies, predictive maintenance is better able to identify the underpinnings of actual problems, enabling technicians to more effectively schedule service at a convenient time.
Precision maintenance
Precision maintenance is the next step in the evolution of predictive maintenance, maintaining a laser focus on equipment reliability and uptime. The goal of precision maintenance is to maximize time between failures or maintenance events and minimize downtime (planned or unplanned), resulting in an increase in productivity and efficiency while lowering overall maintenance costs.
Precision maintenance relies on data, performance analytics and technology such as industrial sensors, and it also incorporates a focus on failure modes, which include complete failure as well operation out of spec. By understanding and prioritizing different failure modes and remedies, precision maintenance can make a tangible difference in your maintenance efficiency and spend.
ATS provides decades of experience in maintenance solutions and technology, and we are ready to work with you to identify the right mix of people, processes and technology to meet your needs, increase uptime and reduce your costs. Contact us to learn more about our industrial maintenance services.


