- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
Permanent magnet motors remain most popular choice for EVs, despite material costs, says report
- December 1, 2022
- News Release
- Electric Vehicles
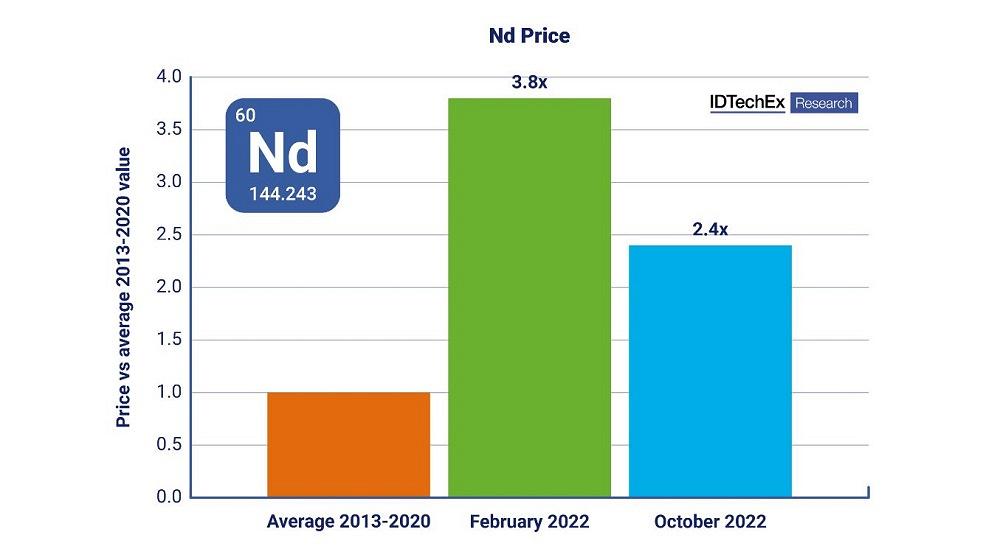
At its peak in 2022, the price of neodymium was 3.8% higher than the average value between 2013-2020.
As the cost of the rare-earth materials used in electric motors continues to rise—neodymium, for instance, cost 2.4 times more in October 2022 than in 2020— some automakers have shifted to alternative motor technologies that don’t rely on rare earths. But the entire market has not made a major turn in that direction.
IDTechEx has released a report, “Electric Motors for Electric Vehicles 2022-2032,” that explores this issue. The report takes a deep dive into the types of electric motors used in EVs, as well as emerging alternatives, and considers several EV markets across China, Europe, and the U.S. It forecasts motor demand over the next 10 years, as well as demand for the materials used in those motors.
To date, the three main motor types used in electric vehicles are permanent magnet, induction, and wound rotor. Permanent magnet motors, which held 86% of the EV motor market in the first half of 2022, use magnets on the rotor that typically are made using rare earths, mostly neodymium. Induction and wound rotor motors use copper windings on the rotor.
There are two main reasons that permanent magnet motors continue to dominate the EV market, in spite of the high cost of neodymium. The first is that the largest domestic EV market is in China, which also supplies the most rare-earth metals, so the cost of neodymium is not as much of a concern as it is in other regions. The other potential reason is that the vehicle platforms sold in 2022 will have been developed over several years. There will be a lag between a rise in market interest for magnet-free motors and their actual deployment on the road.
The report predicts that most of the EV market will remain with permanent magnet motors in the short- to midterm, especially in China. Europe is the key region where adoption of magnet-free technologies could increase.
subscribe now

The Fabricator is North America's leading magazine for the metal forming and fabricating industry. The magazine delivers the news, technical articles, and case histories that enable fabricators to do their jobs more efficiently. The Fabricator has served the industry since 1970.
start your free subscription- Stay connected from anywhere

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Fabricator.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Welder.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Tube and Pipe Journal.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/30/2024
- Running Time:
- 53:00
Seth Feldman of Iowa-based Wertzbaugher Services joins The Fabricator Podcast to offer his take as a Gen Zer...
- Industry Events
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI
Precision Press Brake Certificate Course
- July 31 - August 1, 2024
- Elgin,